Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment in Virtual Reality Exergaming to Regulate Exertion Levels via Heart Rate Monitoring
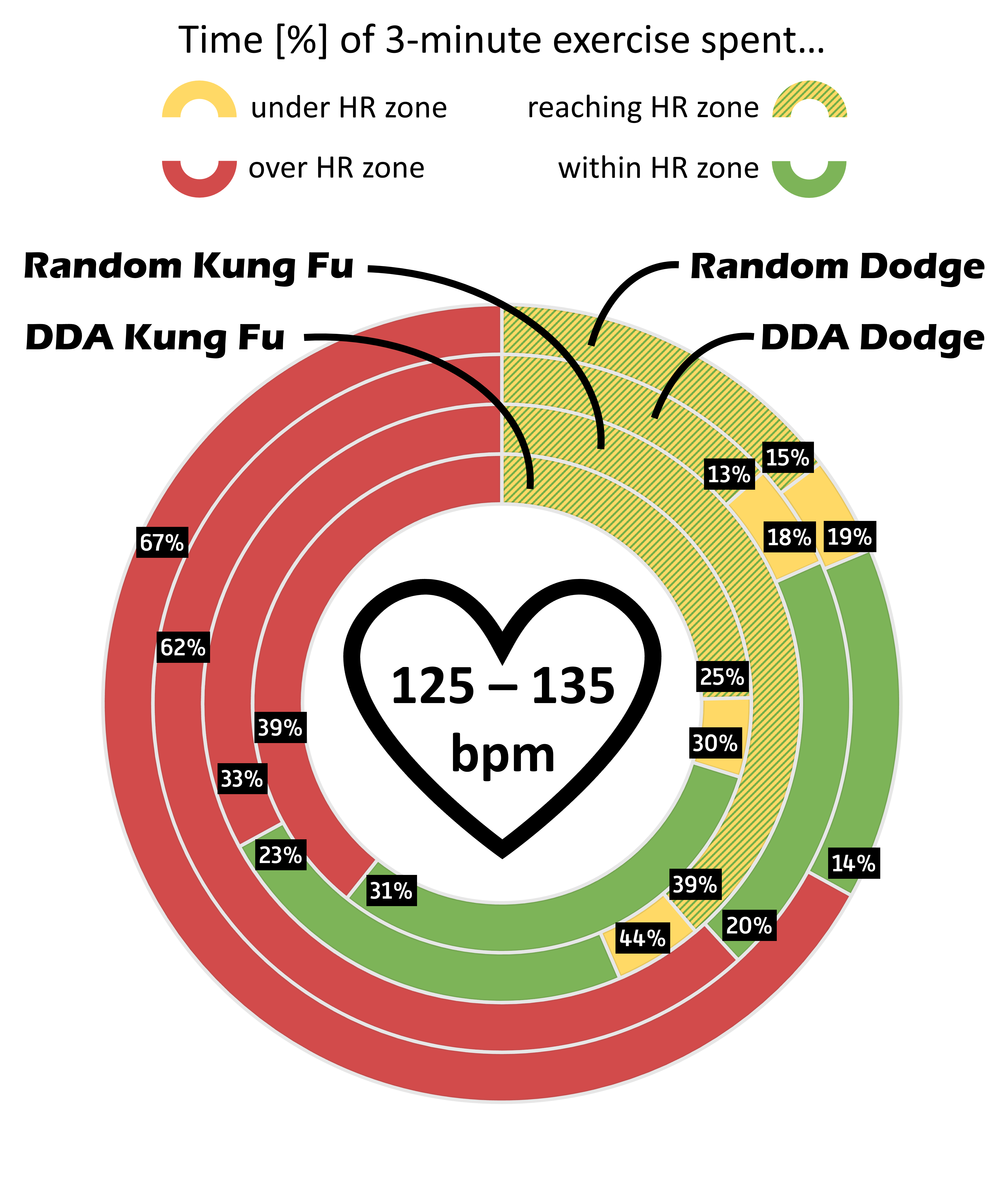
By regulating exertion levels, Dynamic difficulty adjustment (DDA) has the potential to enhance user experience and optimize exercise in Virtual Reality (VR) exergames. This pilot study assesses the effectiveness of adjusting the difficulty of gameplay challenges based on heart rate (HR) data to control the intensity of physical activity in VR exergaming. Observational results from 13 participants indicate that the HR-based DDA more effectively maintained target heart rate zones compared to randomized adjustments. Improved perceived exertion, and increased enjoyment underlines the potential of this approach for VR-based exercise and rehabilitation programs.